Dark Energy Research: New Insights on Universe’s Future
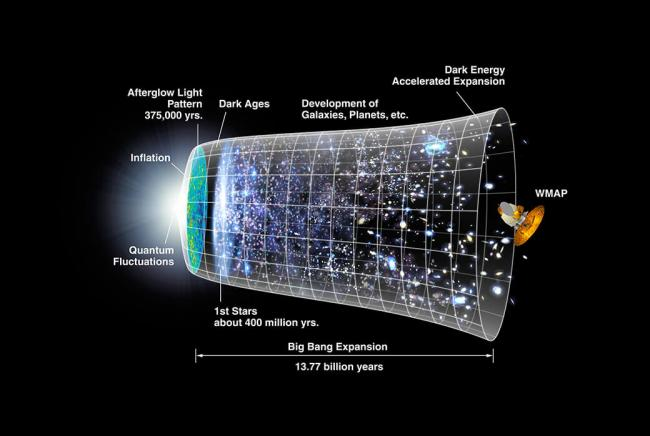
Dark energy research is at the forefront of modern astrophysics, driving a deeper understanding of our universe’s mysterious expansion. With the aid of cutting-edge tools like the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), scientists are uncovering new insights that could redefine our concept of the cosmological constant. Recent findings indicate that dark energy might not be as constant as previously believed, raising intriguing questions about the future of the universe. By constructing the largest 3D map of the cosmos to date, researchers can track how dark energy has influenced the universe’s growth over the last 11 billion years. These dark energy findings not only challenge existing theories but also pave the way for new discoveries in the field of cosmology.
Exploring the enigma of dark energy—often referred to as the force behind the universe’s accelerating expansion—has become a critical focus for astrophysicists. This phenomenon, commonly associated with the cosmological constant, plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of cosmic dynamics. The contributions from initiatives like the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) are invaluable, enabling the creation of intricate 3D representations of the universe. Such observations allow scientists to analyze the subtle shifts in dark energy’s influence over time. As researchers delve into these revelations, they are poised to unravel the complexities of the cosmos that could alter our perception of its future.
Understanding Dark Energy and Its Implications
Dark energy remains one of the most enigmatic components of our universe, heavily influencing its expansion and structure. Current research suggests it might operate like a ‘cosmological constant’—an integral part of Einstein’s theory of general relativity. However, recent findings from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration indicate that the properties of dark energy may not be fixed and could be changing over time. This revelation challenges long-held assumptions in cosmology, suggesting scientists may need to rethink foundational models that explain the behavior and fate of the universe.
The implications of a weakening dark energy are profound. As the universe continues to expand at an accelerated pace, understanding the dynamics of dark energy is crucial for predicting the universe’s ultimate fate. If dark energy is indeed evolving, it alters the balance between attraction and repulsion in cosmic structures, potentially leading to scenarios that differ significantly from predictions based on a static cosmological constant. Thus, the ongoing analysis of dark energy is critical to forming a more accurate picture of the cosmos.
The Role of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is a revolutionary tool in cosmology, aimed at unraveling the mystery of dark energy. Utilizing its unique capabilities, DESI collects data from over 14 million galaxies and quasars, creating the largest 3D map of the universe to date. This massive dataset allows researchers to analyze the influence of dark energy across 11 billion years of cosmic history, providing insights into how it interacts with matter and shapes the universe’s structure. The ability to capture Baryon Acoustic Oscillations, which serve as a cosmic distance marker, enables precise measurements of the ongoing expansion of the universe.
What’s remarkable about DESI is not just its scale, but its collaborative nature. With over 900 researchers across more than 70 institutions, it embodies the global effort to deepen our understanding of dark energy and the cosmos. By sharing results and datasets publicly, the DESI collaboration invites widespread participation from the scientific community, facilitating new discoveries in astrophysics and cosmology. This open-access approach democratizes cutting-edge research, allowing even amateur astronomers and enthusiasts to engage with the data and contribute to our understanding of the universe’s evolution.
The Evolving Nature of the Universe
Research led by the DESI collaboration provides compelling evidence that dark energy, previously thought to be consistent, may be evolving in surprising ways. The analysis reveals that the interplay between dark energy and cosmic matter is complex, suggesting that our understanding of universe expansion must be revisited. By charting data across billions of years, scientists have observed how the distribution of galaxies and large-scale structures in the universe has changed, potentially in response to variations in dark energy.
This evolving perspective underscores the importance of continuous observation and research in cosmology. As researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian engage with the findings of DESI, they contribute to larger discussions regarding dark energy’s historical influence on cosmic development. Each new discovery aids in refining theoretical models and enhancing predictions about future cosmic events, thereby shaping our understanding of the universe’s trajectory.
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations: A Cosmic Ruler
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAOs) are critical to our understanding of cosmic evolution. As sound waves traveled through the early universe, they caused fluctuations in matter density. These fluctuations left an imprint that can be observed today as a regular pattern in the distribution of galaxies. Using this ‘cosmic ruler’, researchers can measure how dark energy has influenced the rate of expansion over cosmic time, aiding in more accurate predictions about the future.
The latest data from DESI has allowed scientists to refine these measurements, providing clarity on the relationship between dark energy and the fabric of our universe. By placing these BAOs within the context of other measurements of expansion, including supernova observations, researchers can triangulate their understanding of dark energy’s evolution. This integration of datasets from various sources emphasizes the collaborative nature of modern cosmology and its reliance on advanced technology to decode the universe’s past and future.
Impact of Dark Energy Findings on Cosmology
The findings of dark energy research conducted by the DESI team shake the foundations of contemporary cosmology. If dark energy’s properties are indeed changing, then the cosmological models that economists and scientists have relied on for decades may require significant revision. This has widespread implications not just for the understanding of the universe but also for the fundamental principles guiding the laws of physics. As current theories struggle to accommodate these new data, they open the door for groundbreaking hypotheses that challenge the status quo.
Moreover, the implications of these findings touch upon philosophical questions about the nature of the universe and humanity’s place within it. As scientists delve deeper into the complexities of dark energy, they are forced to confront not just scientific puzzles but also existential questions about the ultimate fate of the cosmos. Will dark energy continue to drive an accelerating expansion, or could we witness some form of cosmic recalibration? The answers to these questions may redefine humanity’s understanding of time, space, and existence itself.
The Global Collaboration of DESI
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) exemplifies the power of international collaboration in scientific research. With over 900 scientists from more than 70 institutions worldwide, this project brings together diverse expertise to tackle one of cosmology’s most challenging problems: understanding dark energy. The collaboration highlights how pooling resources and knowledge can enhance data collection and analysis, leading to richer insights into the universe’s workings.
In addition to accelerating scientific discovery, this global effort fosters educational opportunities and public engagement. With teams working in various capacities—from data analysis to public outreach—DESI not only advances cosmic research but also aims to inspire future generations of scientists. This commitment to education underscores the importance of science communication in a field where discoveries can fundamentally alter our understanding of the universe.
Exploring Galaxy Evolution Through DESI
Beyond its focus on dark energy, the DESI project also delves into galaxy evolution and the cosmic web. By mapping the distribution of galaxies across large scales, DESI provides essential insights into how galaxies form, evolve, and interact over time. Understanding galaxy evolution is critical for contextualizing the role of dark energy, as the formation and behavior of these celestial bodies are influenced by both gravitational forces and the properties of dark energy.
As researchers analyze the data collected through DESI, they can uncover patterns that reveal the underlying principles of galaxy formation. This research not only enhances our understanding of the universe but also paves the way for future studies in astrophysics. By dissecting these relationships, scientists can more accurately model the history and future of the universe, linking the destinies of galaxies with the enigmatic force of dark energy.
Access to DESI Data and Continued Research
One of the most significant aspects of the DESI initiative is its commitment to open-access data sharing. With the release of its Data Release 1, researchers and the public now have access to extensive datasets detailing millions of galaxies and quasars. This democratization of scientific information encourages a broader range of research opportunities, fostering collaboration and innovation within the scientific community and beyond.
The implications of this accessibility are profound. By allowing independent researchers and even amateur astronomers to explore DESI’s data, the collaboration enhances the potential for new discoveries and insights. As the cosmic map created by DESI continues to expand with nightly observations, the potential for unexpected findings remains high, promising to enrich our understanding of both dark energy and the universe as a whole.
Future Directions in Dark Energy Research
As the DESI project progresses, the future of dark energy research looks promising. The upcoming phases will focus on refining the tools and methods used to analyze dark energy’s impact, improving data collection further and enriching the existing datasets. Future experiments may also seek to probe deeper into cosmic history, stretching beyond the current 11 billion-year timeline explored, which could reveal even more about the nature and evolution of dark energy.
Moreover, integrating findings from DESI with results from other international collaborations could provide a holistic view of the interplay between dark energy, matter, and cosmic structure. As researchers continue to uncover the mysteries surrounding dark energy, new concepts in physics may arise, potentially leading to a groundbreaking shift in our understanding of the universe. The work ahead is not just about answering existing questions but also about inspiring new inquiries into the fabric of reality itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dark energy research and its significance in understanding the universe?
Dark energy research focuses on understanding the mysterious force that drives the accelerated expansion of the universe. It plays a significant role in cosmology, as it is believed to make up about 68% of the universe. Research in this area helps scientists refine their models of the universe, including the cosmological constant, and leads to insights about the ultimate fate of the cosmos.
How does the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) contribute to dark energy research?
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is vital for dark energy research as it creates the largest 3D map of the universe, analyzing over 14 million galaxies and quasars. By examining the distribution of matter, DESI’s findings help elucidate the influence of dark energy over the past 11 billion years, providing critical data on the universe’s expansion.
What are the latest findings from dark energy research using DESI data?
Recent findings from dark energy research utilizing DESI data suggest that the effects of dark energy may be evolving over time, challenging the traditional view of it as a constant force. This revelation prompts a reevaluation of existing cosmological models and contributes to a deeper understanding of how dark energy impacts universe expansion.
In what ways can dark energy findings influence cosmological models?
Dark energy findings can significantly influence cosmological models by providing new insights into how dark energy behaves, potentially leading to revisions of the cosmological constant. As scientists analyze data from DESI and the patterns of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations, they can better predict the future of the universe and its rate of expansion.
What role do Baryon Acoustic Oscillations play in dark energy research?
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations serve as a ‘standard ruler’ in dark energy research, allowing scientists to measure the expansion of the universe over time. By studying the patterns of matter from the early universe, researchers can assess how dark energy has influenced the cosmological landscape and its evolution.
How does the collaboration of researchers enhance dark energy research efforts?
The collaboration within projects like DESI, involving over 900 researchers from more than 70 institutions, enhances dark energy research by pooling diverse expertise and resources. This collective effort accelerates data analysis and interpretation, leading to more robust and comprehensive findings regarding dark energy and its effects on the universe.
Where can I find data related to dark energy research conducted by DESI?
Data related to dark energy research from the DESI collaboration is accessible through its Data Release 1, available for the public to explore. This dataset contains detailed information on millions of celestial objects and serves as a valuable resource for various astrophysical studies.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) involves over 900 researchers from more than 70 institutions globally. |
| Key Findings | Recent results suggest dark energy may be weakening over time, challenging existing models. |
| Research Method | Analysis used the largest 3D map of the universe to study dark energy’s effects over the past 11 billion years. |
| Baryon Acoustic Oscillations | Early universe events created patterns that help measure the impact of dark energy throughout history. |
| Contributions from CfA | CfA played a significant role in algorithm development and cosmological interpretation within DESI. |
| Public Accessibility | DESI Data Release 1 is now available, providing data on millions of cosmic objects for research. |
| Cosmology Goals | CfA researchers also leverage DESI to explore galaxy evolution, the cosmic web, and Milky Way structure. |
Summary
Dark energy research is at the forefront of modern astrophysics, challenging our understanding of the universe’s fate. With the latest findings from the DESI collaboration, we are now confronted with the notion that dark energy could be evolving, potentially reshaping the cosmological principles we’ve relied upon. This evolving landscape of dark energy may hint at the necessity for new theories to explain the universe’s accelerating expansion. As researchers continue to analyze vast datasets and improve our cosmic understanding, we may uncover deeper insights into the very fabric of existence.